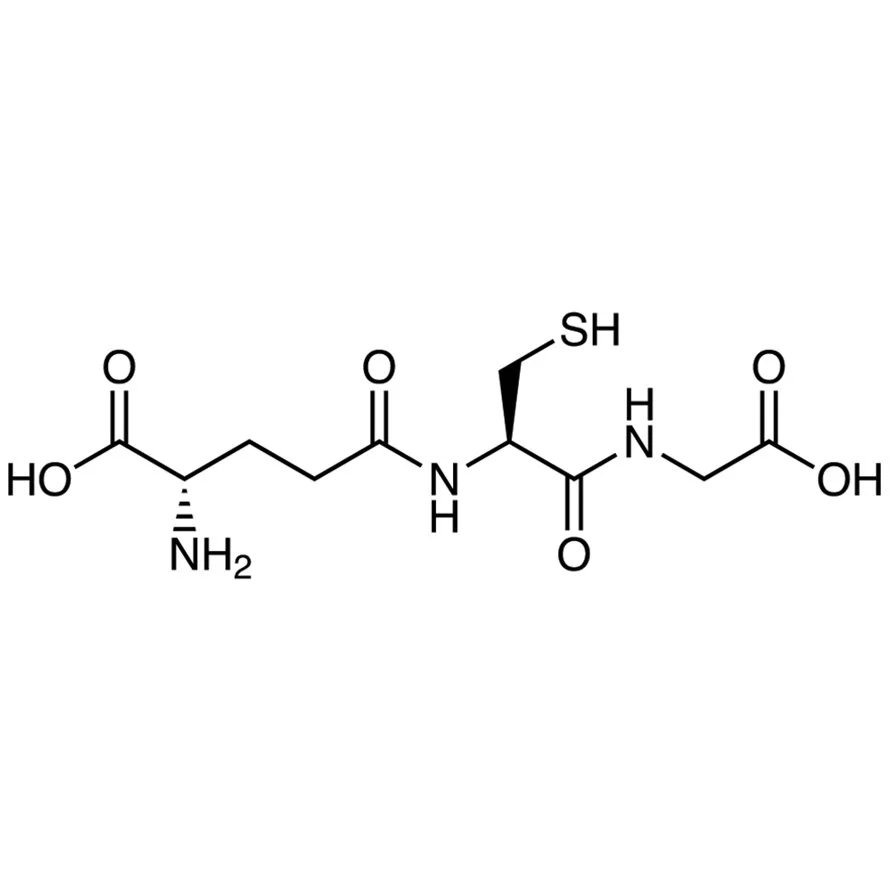
FDA-approved menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) products have seen a dramatic decrease in prescribing practices over the past decade, meanwhile, custom-compounded hormone therapy (CHT) preparations have become more popular.
Read MoreThe US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) published Guidance for Industry #256: Compounding Animal Drugs from Bulk Drug Substances (GFI #256) after careful consideration and significant input from veterinarians, on August 2022. While the guidance specifically addresses compounding from bulk drug substances for animal use, several questions remain. This article aims to provide clarity to some of those questions.
Read MoreThe Food and Drug Administration (FDA) added amoxicillin oral powder for suspension to the drug shortage list and has released guidelines on the creation of compounded versions of specific beta-lactam oral suspension products due to the current lack of amoxicillin oral antibiotic powder for suspension. High demand for amoxicillin oral antibiotic suspension products, coupled with requests for clarification on the preparation of compounded versions, have prompted the Federal Agency to issue compounding recommendations for pharmacists in state-licensed pharmacies and federal facilities not registered as outsourcing sites.
Read MoreAs alluded in a recent declaration that desiccated thyroid extract (DTE) is considered a biologic, FDA may be in the beginning stages of banning compounded desiccated thyroid extract. Compounding pharmacies believe the announcement is a direct threat to the future of compounded thyroid drugs. What remains to be seen is how quickly (or if ever) the federal agency will move to enforce this position. To gauge the future of compounded drug products, one must ask is thyroglobulin considered an inactive ingredient or a biologic?
Read MoreOn November 1, 2022 the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) published the final revision to General Chapter <797> Pharmaceutical Compounding of Sterile Preparations. Compounding pharmacies must clearly understand how the new standards affect their compounding operations and take proper steps to comply. Changes become official on Wednesday November 1, 2023.
Read MorePharmacy compounding is a crucial aspect of the pharmaceutical industry that involves the preparation of customized medications for individual patients based on their specific needs. The compounding process involves various steps, starting from the selection of appropriate raw materials, to the final dispensing of the compounded medication. To ensure the quality and safety of compounded medications, compounding standards have been established by the United States Pharmacopeia (USP). In recent years, regulatory agencies including state boards of pharmacy and FDA have placed increased emphasis on the enhanced regulation of compounding practices.
Read MoreThe information below represents material from the conference and includes data from the 503B Market Landscape Study conducted by the FDA in 2022. These points include emerging compounding trends and key industry insights shared by FDA.
Read More503B outsourcing facilities are required to report adverse events to FDA to stay compliant. 503Bs have noticed an upward trend in audits surrounding adverse events, citing that state boards and the FDA believe adverse events are not being reported properly. This article summarizes 503B responsibilities in reporting adverse events to FDA.
Read MoreCompounding pharmacy business owners find that job ads posted on online employment websites like Indeed and LinkedIn aren't cutting it in today's challenging job market. Even recruiters can't seem to fill positions. Employers are having trouble attracting new employees as well as retaining the talent they have while pharmacy employees lament they want more out of their workplace — a sense of purpose, work/life balance, recognition, appreciation, and advancement opportunities.
Read MoreOn July 22, 2022, the FDA proposed a new rule to update the NDC, or National Drug Code, format from a 10-digit code to a 12-digit code over the next five years citing that the NDC will eventually run out of 5-digit labeler codes within the next 10 to 15 years.
Read MoreOn June 8th 2022, the FDA’s Pharmacy Compounding Advisory Committee, or PCAC, voted 8-5 with one abstention to add glutathione to the final 503A Bulk Drug Substance List. In its evaluation, FDA found there to be a lack of effectiveness and safety data of glutathione and recommended against its inclusion onto the final 503A Bulks List. While PCAC rarely votes against FDA’s direction, that is exactly what happened in this instance.
Read MoreThe FDA Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM) released new guidance in April for compounding drugs from bulk substances for veterinary uses. They state it will help protect animal health by recognizing the need for access to certain compounded medications for animals.
Read MoreThe presence of foreign particulate matter in injectable parenteral drugs is one of the most common reasons for recalls. As the FDA begins to inspect more 503As and 503Bs, there has been a rise in noncompliance observations with inadequate visual inspection. In response, this article aims to help compounders understand how to properly visually inspect injectable drug compounds.
Read MoreFDA announced on March 21, 2022 that the US is currently experiencing an interruption and shortage in the supply of prefilled 0.9% sodium chloride (saline) IV lock/flush syringes because of the COVID-19 supply chain challenges during the pandemic and beyond. Could prefilled 0.9% sodium chloride flush syringes be a drug for compounders to develop and fill the gap in the supply chain?
Read MoreCleanrooms must be purpose-built in order to achieve regulatory compliance and quality assurance. A retail pharmacy with plans to squeeze in a small area to prepare TPN or specialty IV compounds may find out the hard way that there was not enough space allotted to promote operational efficiencies. Similarly, a 503A pharmacy looking to convert to a 503B outsourcing facility may be in for a rude awakening to learn that cleanroom designs and space requirements are vastly different for each entity. However, the following principles hold true for most cleanroom layout design and cleanroom construction planning:
Read MoreIn a status report filed March 3rd with the U.S. District Court for D.C., FDA will suspend the implementation of the MOU (Memorandum of Understanding) and engage in a formal rulemaking process. This is a huge win for compounding pharmacies and the industry – the FDA will conduct a formal notice-and-comment rulemaking to implement its MOU with states for interstate shipments of compounds.
Read MoreOn February 16th, the FDA published an alert for healthcare professionals regarding safety reports involving the use of compounded intranasal ketamine nasal spray, which could put patients at risk. FDA says they have concerns about increased potential risk of adverse events, misuse, and abuse associated with compounded ketamine nasal spray.
Read MoreProviding clinical trial services can yield a high return on investment. While CROs and CDMOs may be the first choice for conducting many clinical studies, some sponsors choose to partner with compounding pharmacies or outsourcing facilities. Pharmacies and outsourcing facilities that would like to provide clinical trial services should be aware of the different regulatory requirements and heightened quality assurance expectations. This article introduces compounders to the possibility of adding clinical trial services to their offerings.
Read MoreA new proposal for USP 797 was released in September of 2021 for stakeholder review and comment. Pharmacies wanting to apply extended BUDs to their CSPs will be particularly impacted. Stakeholders have argued that many of the additional requirements for extended BUDs closely resemble some GMP processes and controls that 503Bs have to abide by. Others have debated that the 250-unit cap is arbitrary, cost-prohibitive, and will decrease patient access.
Read MoreAs independent pharmacies continue to struggle with declining reimbursements, compounding could be one way to enhance profitability. The average compounding-only pharmacy enjoys a net profit of around 20%, while a retail pharmacy may only see about 3%. Compounding pharmacies are primarily cash-based businesses that are not subject to third-party audits or DIR clawbacks. For these reasons, pharmacies may want to add compounding to the mix.
Read More